
Ethiopian plane received repeated nose-down commands
Apr 04, 2019
In a tragic incident involving an Ethiopian Airlines flight, the aircraft received repeated nose-down commands from its automated flight control system shortly after takeoff. This malfunction was linked to the aircraft's Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System, designed to prevent stalling. Despite the pilots' attempts to regain control, they faced significant challenges as the system continued to force the nose downward. This series of events ultimately led to the plane's crash, raising concerns about pilot training, system design, and regulatory oversight in aviation safety. The incident underscored the critical need for improvements in both technology and human factors in cockpit operations.
Understanding the Ethiopian Plane Incident
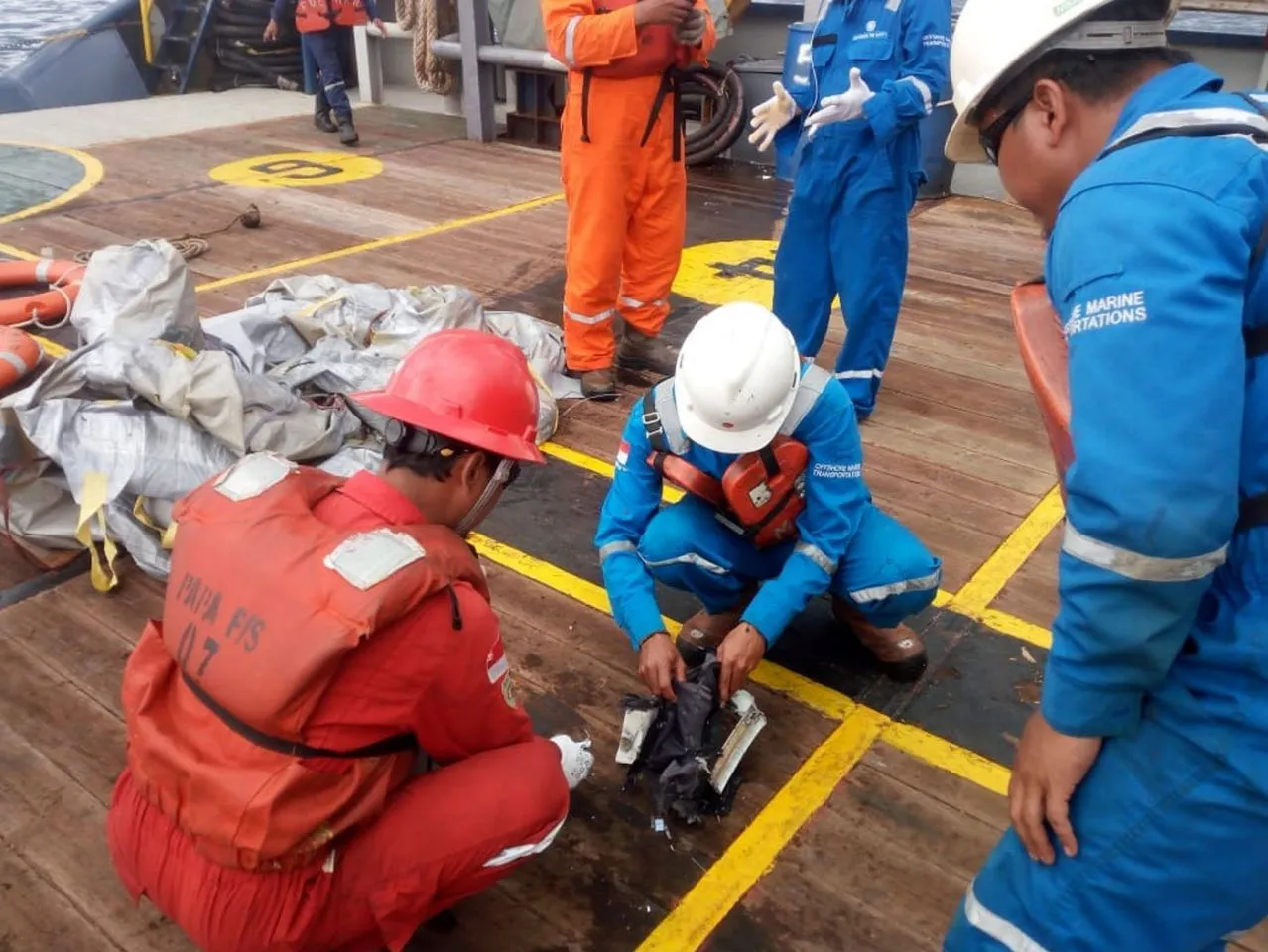
The tragic Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302 disaster on March 10, 2019, raised significant concerns regarding aviation safety and the design of the Boeing 737 MAX aircraft. Investigations revealed that the aircraft received repeated nose-down commands, which played a critical role in the accident. This article delves into the details of the incident, the technology involved, and the implications for the aviation industry.
The Role of MCAS in the Ethiopian Plane Incident
One of the key factors identified in the Ethiopian Airlines crash was the Maneuvering Characteristics Augmentation System (MCAS). This system was designed to automatically adjust the aircraft’s pitch to prevent stalling, particularly in high angles of attack. However, in both the Ethiopian Airlines and Lion Air crashes, the MCAS system was activated erroneously due to faulty sensor data.
Repeated Nose-Down Commands Explained
During the flight, the Ethiopian Airlines plane received repeated nose-down commands from the MCAS, which caused the pilots to struggle to regain control. The automation system was designed to enhance safety but instead contributed to the tragedy. The pilots received alerts indicating an unusual attitude, and despite their efforts to counteract the MCAS commands, the plane ultimately crashed.
Investigation Findings and Recommendations
The investigation into the Ethiopian Airlines crash, led by the Ethiopian Civil Aviation Authority and supported by international agencies, highlighted several critical areas for improvement. The final report recommended enhanced pilot training, improved maintenance protocols, and a thorough review of the MCAS system. These recommendations aim to prevent similar incidents in the future.
Chart: Key Findings from the Investigation
| Finding | Description |
|---|---|
| MCAS Activation | MCAS was activated due to erroneous sensor data, causing repeated nose-down commands. |
| Pilot Response | Pilots struggled to regain control against automated commands. |
| Training Gaps | Insufficient training on the MCAS system contributed to the pilots' difficulties. |
| Maintenance Issues | Regular maintenance checks and protocols were highlighted as areas needing improvement. |
Impact on Aviation Safety Regulations
The Ethiopian Airlines incident has had far-reaching implications for aviation safety regulations worldwide. Regulatory bodies, including the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the European Union Aviation Safety Agency (EASA), have implemented stricter oversight of aircraft design and pilot training programs. The goal is to ensure that such tragedies do not occur again.
Industry Response and Changes
After the Ethiopian Airlines crash, Boeing faced significant scrutiny regarding the safety of the 737 MAX. The company took several steps to address the concerns raised by the incident, including software updates to the MCAS system and enhanced pilot training programs. Furthermore, airlines operating the 737 MAX were required to undergo thorough inspections to ensure compliance with new safety standards.
Global Repercussions and Public Trust
The fallout from the Ethiopian Airlines disaster extended beyond regulatory changes. Public trust in aviation safety was significantly impacted, leading to increased scrutiny of aircraft manufacturers and airlines alike. Passengers became more aware of safety protocols and the technologies that govern modern aviation.
Conclusion: Lessons Learned
The Ethiopian Airlines Flight 302 tragedy serves as a stark reminder of the complexities of modern aviation and the critical importance of safety in aircraft design and operation. The repeated nose-down commands issued by the MCAS system underline the need for rigorous testing, training, and oversight in the aviation industry. As we move forward, the lessons learned from this incident must guide future developments to ensure the safety of all passengers.
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, while the Ethiopian Airlines incident was a devastating event, it prompted necessary changes and discussions surrounding aviation safety. The continual evolution of technology and regulatory practices must prioritize the safety of passengers and crew above all else. Through these efforts, the aviation industry can work to restore public confidence and ensure that similar tragedies remain a thing of the past.
Related Articles
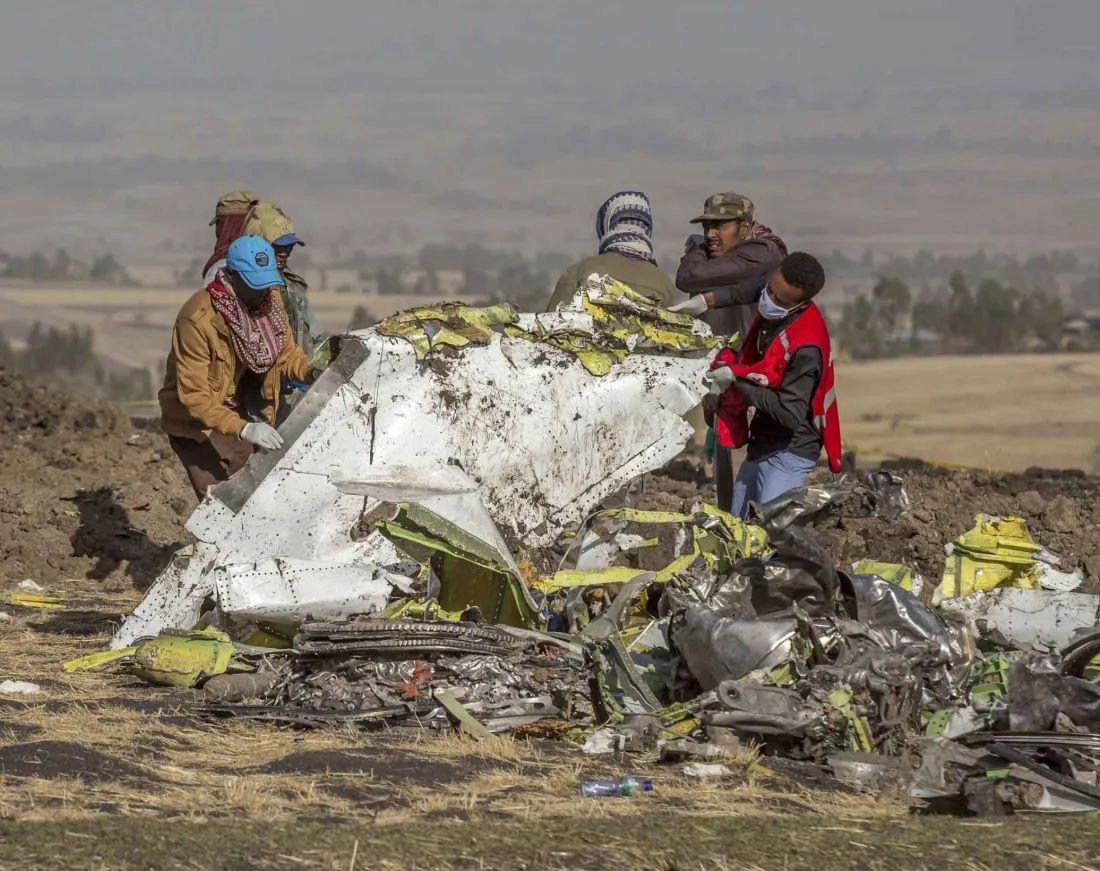

Why the Boeing fiasco will not kill the 737 MAX.

Virgin delays Boeing 737 MAX deliveries

US regulator lifts grounding of the Boeing 737 MAX

US NTSB Criticizes Ethiopian MAX report

Survey finds 1 in 5 will never be comfortable flying the MAX

Southwest says getting MAX fleet airborne will take up to two months

Reports that 737 MAX safety options are lucrative are nonsense

Ratings agencies cut Boeing outlook to negative

Pilot training, skill levels and automation come under intense scrutiny

Passengers urged not to let MAX problems undermine trust in aviation
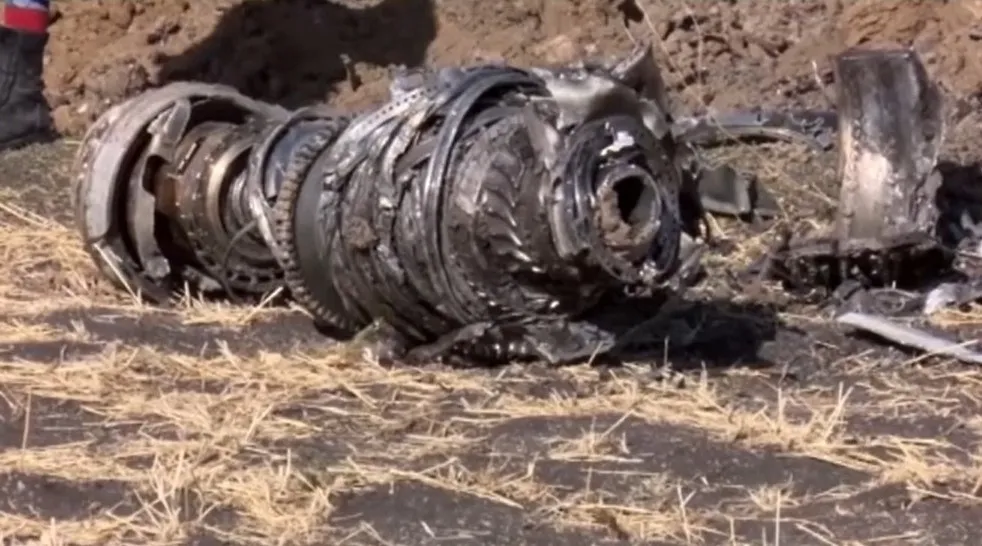

Nine regulators join Boeing 737 MAX review

Major regulators join international panel reviewing the 737 MAX

Major boost for Boeing as Alaska opts for more 737 MAX jets.

Lion Air investigators confirm presence of third pilot

Is the US congressional report on the 737 MAX flawed?

Investigators believe MCAS involved in both Boeing crashes, says report
