
MH370: Chronology of major events
Nov 30, 2021
Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370, a Boeing 777, disappeared on March 8, 2014, during its journey from Kuala Lumpur to Beijing with 239 people on board. Shortly after takeoff, the plane lost contact with air traffic control, deviating from its flight path. Initial search efforts focused on the South China Sea but later shifted to the Indian Ocean after satellite data suggested a different trajectory. Despite extensive searches and international cooperation, the wreckage was found scattered over remote ocean areas, with only a few pieces confirmed as belonging to the aircraft. The disappearance remains one of aviation's greatest mysteries, with no definitive conclusion.
On March 8, 2014, Malaysia Airlines Flight MH370 vanished from radar screens, triggering one of the most extensive search operations in aviation history. The disappearance of the Boeing 777 has left many questions unanswered. Here, we present a detailed chronology of major events related to the flight's disappearance, offering insights for those interested in the mystery of MH370.
Chronology of Major Events
Understanding the timeline of events can provide clarity on the circumstances surrounding MH370's disappearance. Below is a table outlining key occurrences related to the flight:
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| March 8, 2014 | Flight MH370 takes off from Kuala Lumpur International Airport at 12:41 AM local time. |
| 1:07 AM | The last communication from the cockpit occurs: "Good night, Malaysian three-seven-zero." |
| 1:21 AM | The aircraft disappears from air traffic control screens. |
| 8:00 AM | Malaysia Airlines reports the plane missing after failing to arrive in Beijing. |
| March 9, 2014 | Search efforts begin, focusing on the South China Sea. |
| March 15, 2014 | Search area shifts to the Indian Ocean after satellite data suggests a different flight path. |
| March 24, 2014 | Malaysian Prime Minister Najib Razak announces that the flight ended in the southern Indian Ocean. |
| April 2014 | Search operations expand to a vast area of the Indian Ocean, with over 26 countries involved. |
| July 29, 2015 | A piece of debris, a flaperon, is found on Réunion Island, confirming the plane's crash in the Indian Ocean. |
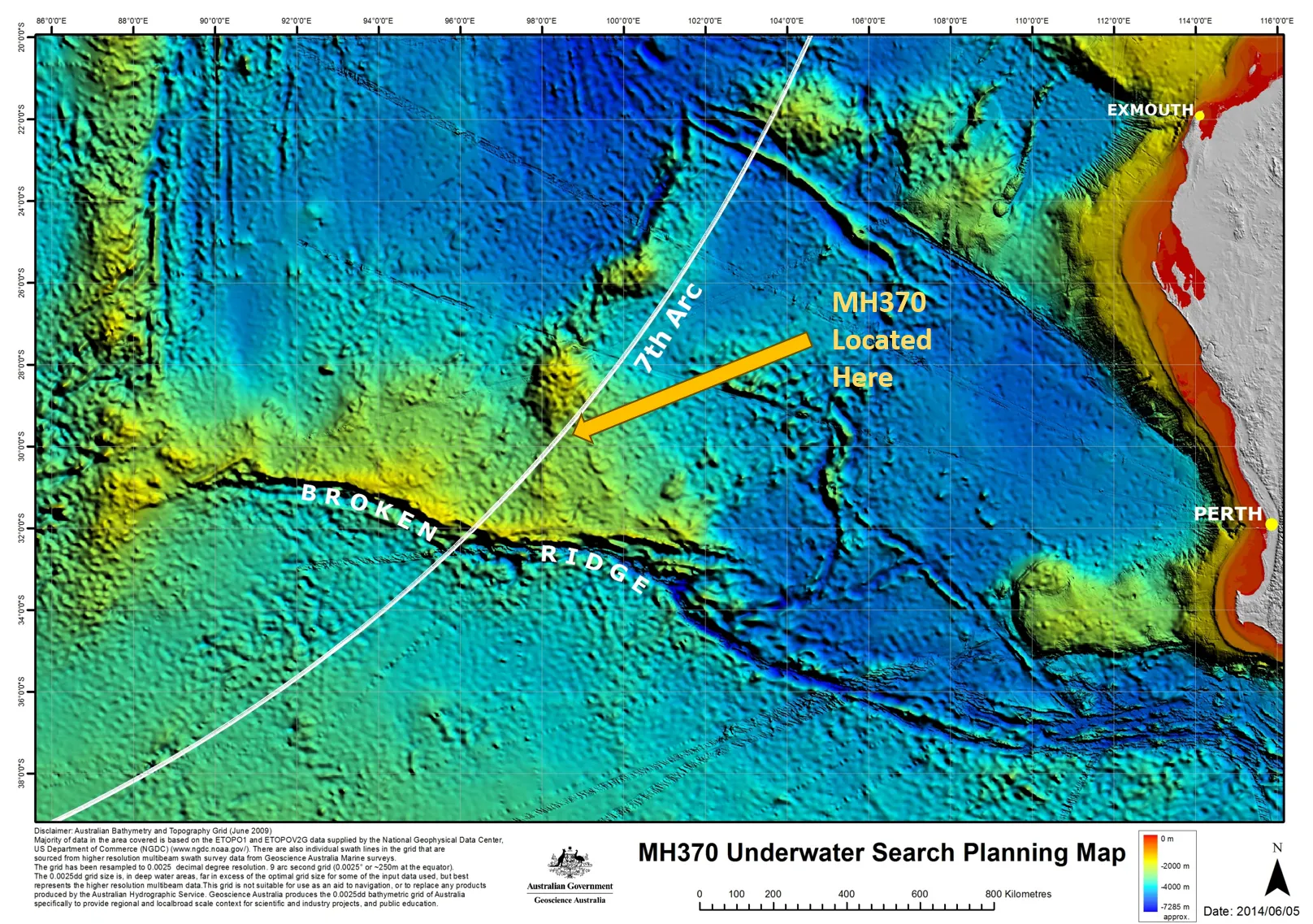
| October 2017 | The search for MH370 is officially suspended after an extensive underwater search yields no results. |
| January 2018 | Ocean Infinity, a private company, begins a new search effort under a "no find, no fee" agreement. |
| April 2018 | Ocean Infinity's search ends without discovering further wreckage. |
This timeline illustrates how the search for MH370 expanded from initial efforts in the South China Sea to an extensive, international operation in the Indian Ocean. The search involved numerous countries and organizations, highlighting the global interest in the mystery of this flight.
Key Theories and Developments
As the search for MH370 progressed, several theories emerged regarding the cause of the disappearance. Some of the most discussed theories include:
- Hijacking: Some experts believe that the aircraft may have been hijacked, as indicated by the unusual flight path taken after its last communication.
- Pilot Involvement: Investigators considered the possibility that the pilot or co-pilot may have intentionally diverted the aircraft.
- Mechanical Failure: Another theory suggests that a catastrophic mechanical failure could have led to the plane's disappearance.
Despite these theories, no definitive evidence has been found to support any single explanation. The lack of recovered wreckage has only fueled speculation and conspiracy theories. The mystery remains one of the most perplexing in modern aviation history.
Impact on Aviation Safety
The disappearance of MH370 has had significant implications for aviation safety and protocols. Following the incident, several measures have been implemented to enhance flight tracking and communication:
- Global Tracking Systems: The International Civil Aviation Organization (ICAO) has recommended implementing global flight tracking systems to monitor aircraft in real time.
- Emergency Locator Transmitters (ELTs): Improvements have been made to ELTs to ensure they activate automatically and transmit signals for longer periods.
- Increased Communication Protocols: Airlines have updated protocols for cockpit communication and emergency procedures.
These changes aim to prevent similar incidents in the future and enhance overall safety in the aviation industry.
Conclusion
The saga of MH370 remains unresolved, with many questions still lingering. The chronology of events highlights the complexity and challenges associated with the search for the missing flight. The ongoing interest in MH370 serves as a reminder of the need for continuous improvement in aviation safety and emergency response protocols. As new technologies emerge, there is hope that further advancements will provide answers and ensure the safety of passengers around the globe.
Related Articles

Yet more theories about MH370 debunked.

World Expert; Not finding MH370 risks more lives
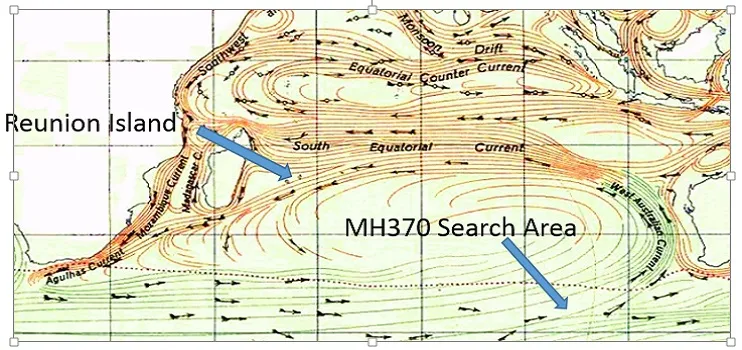
Will reverse drift modelling find MH370?
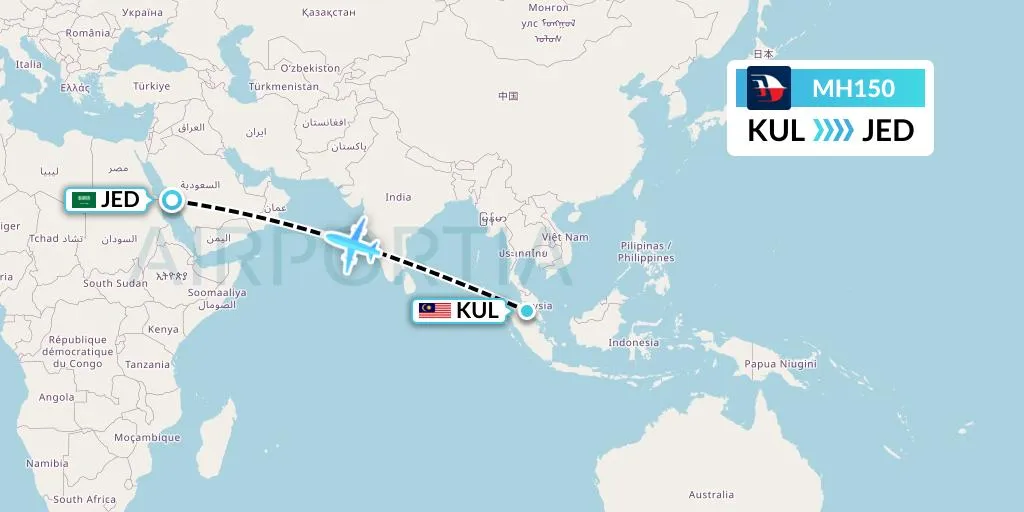
Was MH150 The Intended Target Not MH370?

Vanished plane not without precedent

US safety veteran backs call for MH370 search to be extended.

UPDATED: New MH370 study suggests it's further north

Updated: New MH370 search area not specific enough, says Minister.

Updated: MH370 ship heads towards search area

Unprecedented MH370 findings boost pressure to resume search

Underwater search vehicle to be deployed in MH370 search

Timeline for MH370
Thomas Discusses MH370 Report On Skynews
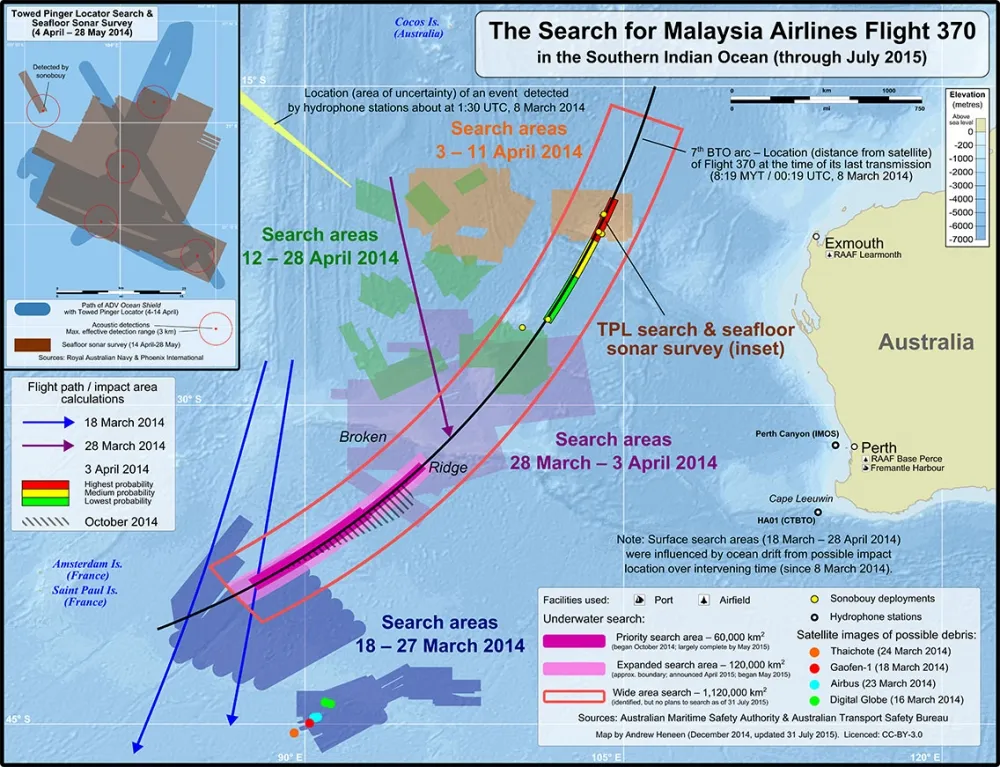
The beginning of the end of the MH370 search

Suitcase also found near piece of wing, is it from MH370?

Startling revelations demand a reopening of MH370 investigation
